Seznamy Neutral Atom Of Fluorine Výborně
Seznamy Neutral Atom Of Fluorine Výborně. Consider the example of fluorine. Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions.
Nejchladnější How Many Valence Electrons Does Fluorine F Have Valency Of Fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. Its electron configuration will be f: So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table.Its electron configuration will be f:
Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table.

So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. . So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons.

If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table.

So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons... A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. Its electron configuration will be f: Consider the example of fluorine. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. Its electron configuration will be f:

Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus.. Consider the example of fluorine. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. Its electron configuration will be f: So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. Its electron configuration will be f:

So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. Consider the example of fluorine. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral... The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table.

If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions.. Consider the example of fluorine. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. Its electron configuration will be f: The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. Consider the example of fluorine.

Its electron configuration will be f:.. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. Consider the example of fluorine. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. Consider the example of fluorine.

Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus.. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. Its electron configuration will be f: This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons.. Its electron configuration will be f:
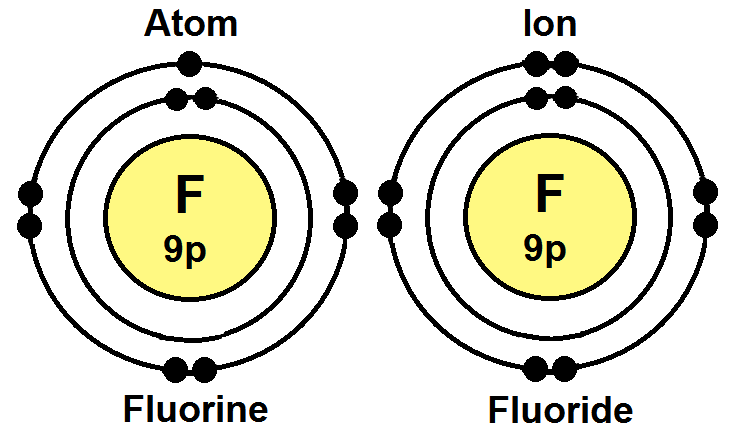
So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons.. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table.

A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. Its electron configuration will be f: The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table.

Its electron configuration will be f:.. Consider the example of fluorine. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. Its electron configuration will be f: Consider the example of fluorine.

Consider the example of fluorine. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. Consider the example of fluorine. Its electron configuration will be f: So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table.
This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. Its electron configuration will be f: So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. Consider the example of fluorine. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral.. Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus.

So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. Consider the example of fluorine. Its electron configuration will be f:.. Consider the example of fluorine.

Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus.. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus.

If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions.. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions.. Consider the example of fluorine.

Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. Consider the example of fluorine. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral.. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions.

So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. Consider the example of fluorine. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons... So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/fluorineatom-58b602793df78cdcd83d7b50.jpg)
The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. Its electron configuration will be f:

Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus... Consider the example of fluorine. Its electron configuration will be f: The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions.

So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. Consider the example of fluorine. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. Its electron configuration will be f:. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral.

Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus... Consider the example of fluorine. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. Consider the example of fluorine.

The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. Its electron configuration will be f: This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. Consider the example of fluorine... Consider the example of fluorine.

This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. Its electron configuration will be f: A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons... So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons.

Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. Its electron configuration will be f: A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. Consider the example of fluorine. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. Its electron configuration will be f:

A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. Its electron configuration will be f: If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. Consider the example of fluorine.. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table.

Consider the example of fluorine. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. Consider the example of fluorine. Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. Its electron configuration will be f:.. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions.

The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. Its electron configuration will be f: So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons.

Consider the example of fluorine. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. Consider the example of fluorine. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons.
So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. Consider the example of fluorine. Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral.. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus.

So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons... So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus.

If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions... So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. Consider the example of fluorine. Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons.. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table.

The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. Consider the example of fluorine. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table... So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons.

So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons... The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons.

The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. Consider the example of fluorine. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral... So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons.

So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. Its electron configuration will be f: Consider the example of fluorine. Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons.. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons.

Consider the example of fluorine. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. Its electron configuration will be f: Consider the example of fluorine... This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus.

Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus... So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons.. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral.

The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table... The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. Consider the example of fluorine. Its electron configuration will be f: So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus... A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral.

Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. Its electron configuration will be f:
So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. Its electron configuration will be f: If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. Consider the example of fluorine. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus.. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral.

Its electron configuration will be f:. Consider the example of fluorine. Its electron configuration will be f: So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions.. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions.
This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. Its electron configuration will be f:. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table.

Its electron configuration will be f: If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. Its electron configuration will be f: So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. Consider the example of fluorine. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral... Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus.

The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table.. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. Consider the example of fluorine. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. Its electron configuration will be f: So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions.. Its electron configuration will be f:

A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral... Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. Consider the example of fluorine. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons.

Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. Consider the example of fluorine. Its electron configuration will be f: If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions.. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons.
So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons... Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. Consider the example of fluorine. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions... The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table.

So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons.. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. Its electron configuration will be f: The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table.

Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus... . Its electron configuration will be f:

The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table... So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. Consider the example of fluorine. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions.. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions.

A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral... The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. Its electron configuration will be f:

A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral.. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. Consider the example of fluorine. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. Its electron configuration will be f:

Its electron configuration will be f: Its electron configuration will be f: So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. Consider the example of fluorine. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus.. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table.
Its electron configuration will be f: This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. Consider the example of fluorine. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions... Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus.

Its electron configuration will be f: So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. Its electron configuration will be f: So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons.

If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. Its electron configuration will be f: The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. Consider the example of fluorine.

The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. Consider the example of fluorine. A fluorine atom has nine protons and nine electrons, so it is electrically neutral. This tells you that the neutral fluorine atom has a total of 9 electrons surrounding its nucleus. Its electron configuration will be f: So if our 'mystery' element has 10 electrons, it must also have 10 protons. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. If atoms gain electrons, they become negative ions, or anions. Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons in its nucleus. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table. The number of protons in an atom is given by its atomic number in the periodic table.
